The Arbotom sonic tomograph (also known as the Arbotom stress wave tomograph) is a tomography device for analysis of the material properties of wood. The new features of the Arbotom 6 allow for data collection of measured stress wave time of flight, modulus of elasticity (MOE), 2 dimensional and 3 dimensional plane measurements on tree trunks, and tree root detection and mapping. Below are some of the useful measurement outputs by the Arbotom. The measurable data makes it an ideal solution for forestry and timber research.
Utilized in a Wide Range of Published Research on Trees and Timber
- 3D Imaging of Tree Cavities: Development of 3D viewers for internal cavities using pulse ultrasound data acquired from Arbotom.
- Decay Detection Accuracy: Methods for improving the accuracy of decay detection in trees, particularly in species like Picea abies.
- Sonic Diagnostics: Evaluation of internal tree tissue condition in various species such as Cupressus using Arbotom’s acoustic tomography.
- Urban Tree Health Monitoring: Non-destructive testing of internal tree conditions in urban environments to monitor safety and health, including cavity and decay detection.
- Timber Quality Assessment: Use of Arbotom for qualitative assessment of harvested timber, including defect and internal structure analysis.
- Forest Management Decision Support: Application of Arbotom in supporting forest management decisions, especially in protected areas, by detecting internal decay and structural issues in hardwood trees.
- Influence of Environmental Factors: Research on how moisture content, density, and external factors affect stress wave velocity and tree integrity, measured with Arbotom.
- Post-Fire Tree Condition: Analysis of wood quality and vitality of trees in burned areas using Arbotom for stress wave transmission data.
- Infection and Disease Diagnosis: Acoustic tomography used to assess the extent of pathogenic damage in tree trunks, such as in Magnolia and Sequoiadendron species.
- Historic Tree and Timber Structure Analysis: Application of Arbotom to assess the internal integrity of trees and timber structures of historic value, particularly in architectural conservation.
- Root System and Urban Tree Assessment: Utilization of Arbotom for the non-invasive analysis of tree root systems and anchorage in urban environments.
- Biomechanical Analysis of Trees: Evaluation of the mechanical properties of wood, such as elasticity and dynamic modulus, in relation to internal defects in living trees using Arbotom.
- Ecological Research on Forest Decay: Studies examining the spatial distribution of internal decay in tree species, particularly in riparian and desert forests, using stress wave technology.
- Tree Age and Health Correlations: Use of Arbotom in monitoring the health and structural integrity of old and monumental trees, supporting long-term conservation efforts.
- Biodiversity and Conservation Studies: Arbotom applied in research correlating tree decay with surrounding biodiversity, such as saproxylic beetle populations, to understand ecological interactions.
This list reflects the versatility of Arbotom in diverse research fields, ranging from forestry and timber quality control to ecological conservation and urban tree management. An extensive list of similar published research is available by searching on Google Scholar.
Here are key elements of the Arbotom Sonic Tomograph:
How it Works:
- Sonic Wave Transmission:
- The device sends sound waves through the tree or timber, and sensors placed around the trunk or the timber structure measure the time it takes for the waves to travel between various points.
- The speed (velocity) of the sound waves is influenced by the density of the material they travel through:
- High velocity indicates solid, healthy wood.
- Low velocity suggests decay, hollows, or cracks.
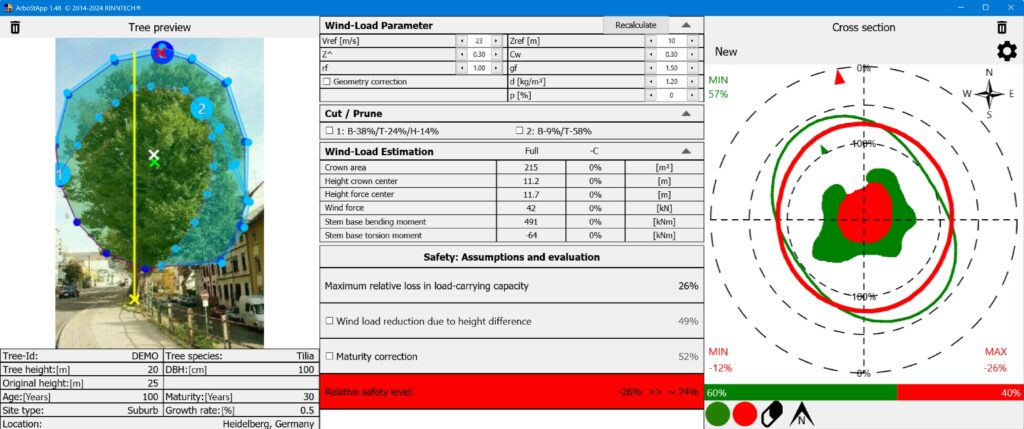
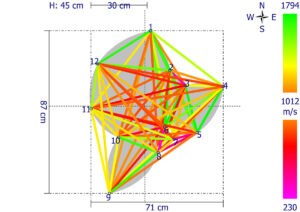
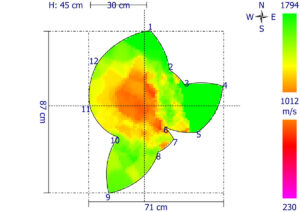
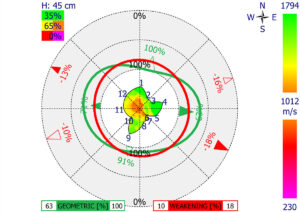
- Tomographic Imaging:
- Based on the time of flight (velocity) of the sonic waves, the system generates a cross-sectional image (tomogram) of the internal structure.
- These images use different colors to represent various states of wood integrity. For example:
- Blue or green often indicates healthy, sound wood.
- Red or yellow may represent defects such as decay or cavities.
- The images are processed to show a 2D or 3D model of the tree’s internal condition.
Applications:
- Tree Risk Assessment:
- Arborists use Arbotom to assess tree stability and health, especially in urban environments where trees may pose risks to public safety. It helps in deciding whether a tree needs to be pruned or removed.
- Timber Structure Analysis:
- It’s used in forestry and the timber industry to evaluate the quality of wood before harvesting or construction. Detecting internal flaws early can prevent the use of compromised timber in building projects.
- Tree Conservation:
- For protected or historic trees, Arbotom is ideal as it minimizes harm during assessment, ensuring long-term conservation efforts are not jeopardized by invasive tests.
Benefits:
- Non-Destructive Testing: Since no cutting or drilling is required, the technique preserves the tree’s health and integrity while providing accurate internal data.
- 3D Visualization: Arbotom’s ability to create 3D models offers a complete picture of the tree’s internal structure, making it easier for arborists and engineers to make informed decisions.
- Early Detection: It can detect early signs of decay or structural weakness, helping with preventive care and risk management.
Tree Root Detection and Mapping with the Arboradix Unit
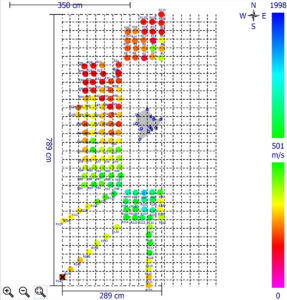
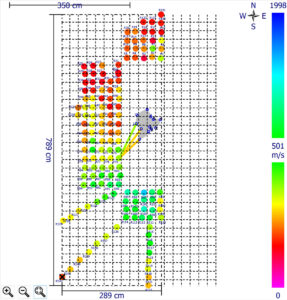
Tree root detection is made possible with the unique addition of the Arboradix unit for the Arbotom sonic tomograph system. It comes included with the Arbotom Expert and Scientific models. The Arboradix sensor and steel rod is placed at the measurement location. A rubber mallet is used to apply a tap to the top of the steel rod and the resulting stress wave is transmitted through the rod into the soil or material below.
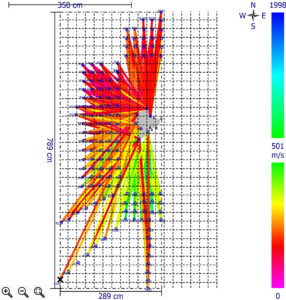
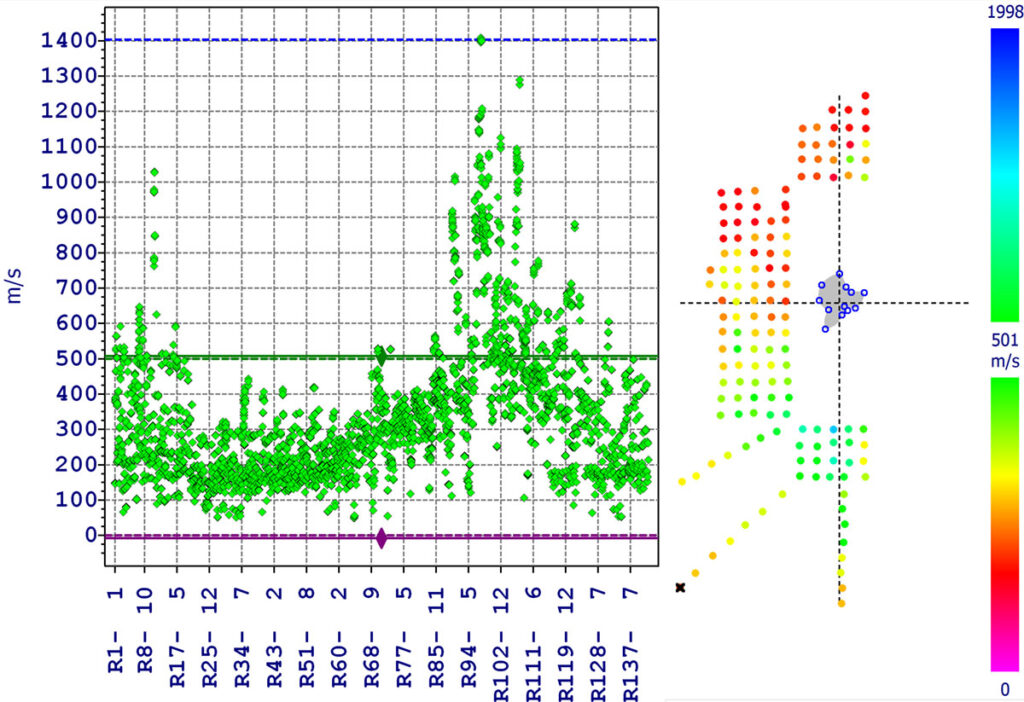
Allows for Stress Wave Statistical Data Analysis
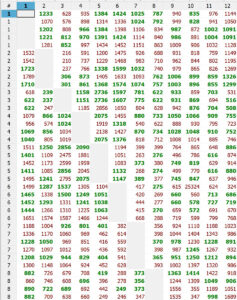
The Arbotom software allows for raw data analysis and filtering options for measured velocities as well as adjustable statistical analysis for additional filtering as needed. The software interface includes a specific module for tree root detection and and analysis.
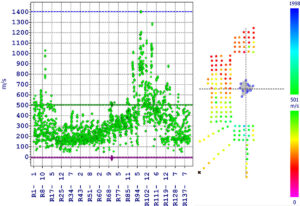
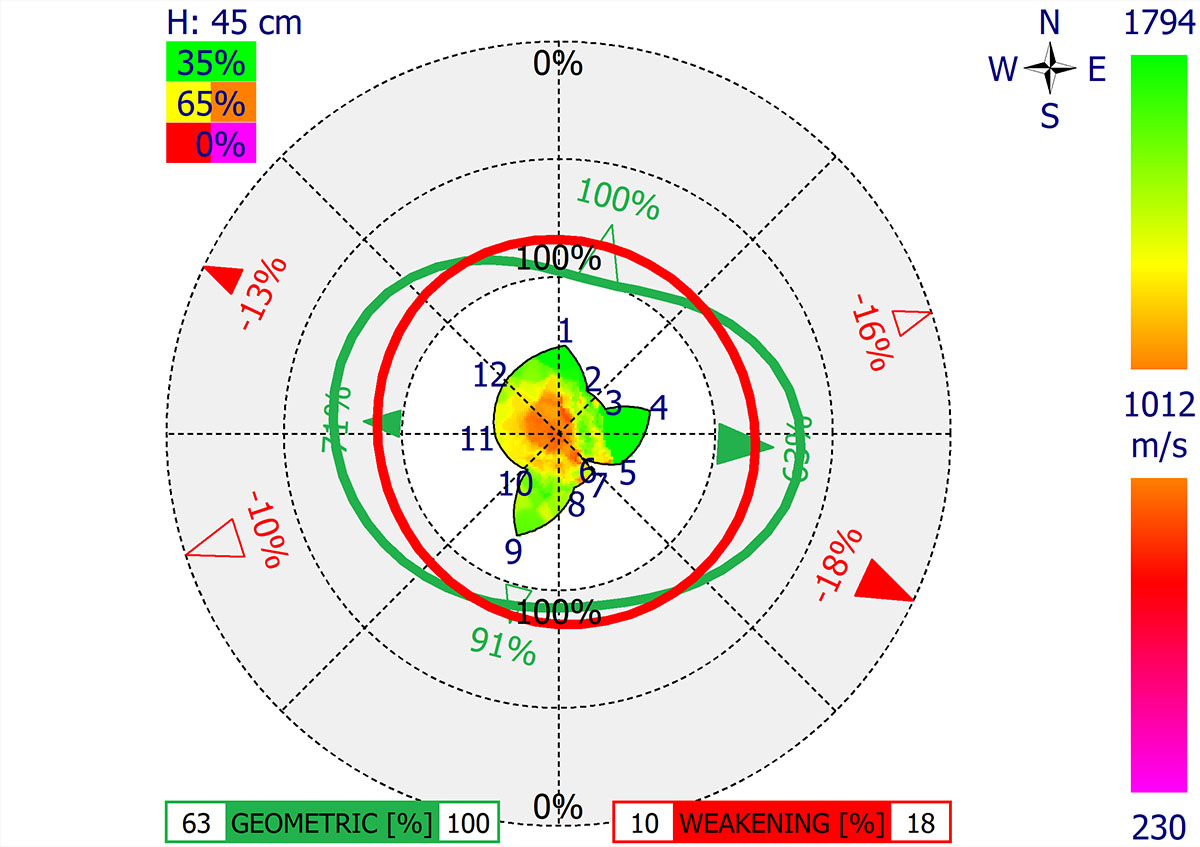
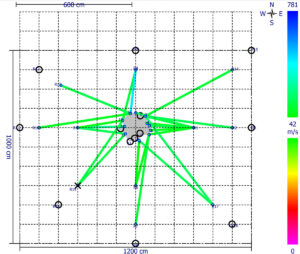
Defining the Tree Root Area with the Arbotom and Arboradix
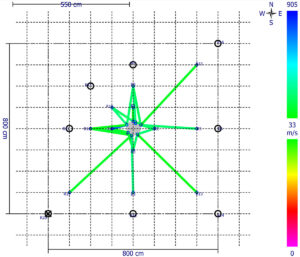
The Arbotom sonic tomograph is capable of identifying where tree roots may or may not exist. Hence it can be used for estimating the tree root area for trees. If a tree root isn’t identified at or near a measured location, the result shows a black circle. A common practice is to carry out the measurement in 8 directions for estimation of the tree root area.
This is not only useful for research, but also has practical applications. For example, it can be used to define the Tree Protection Zone (TPZ) during construction and development planning.
The Arbotom is a powerful tool in both tree care and timber analysis, combining advanced technology with practical applications to enhance safety, tree preservation, and wood quality assessment. This can be the perfect tool for many research goals. See below for product specifications and how to inquire.